
Transformative Journey of GST @ 7 Years: Unifying India’s Tax System for Economic Growth and Transparency
By: Admin|Date: August 11, 2024|Categories: 7 Years of GST
Introduction
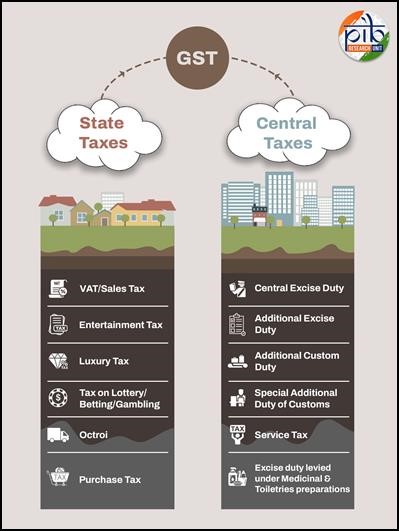
On July 1, 2017, India witnessed a historic shift in its tax system with the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST). This reform, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi as a “path-breaking legislation for New India,” replaced a fragmented and complex indirect tax regime, which had previously burdened businesses and consumers with multiple taxes such as excise duty, service tax, VAT, and CST. The introduction of GST marked a significant step towards simplifying compliance, reducing the cost of doing business, and eliminating interstate tax barriers.
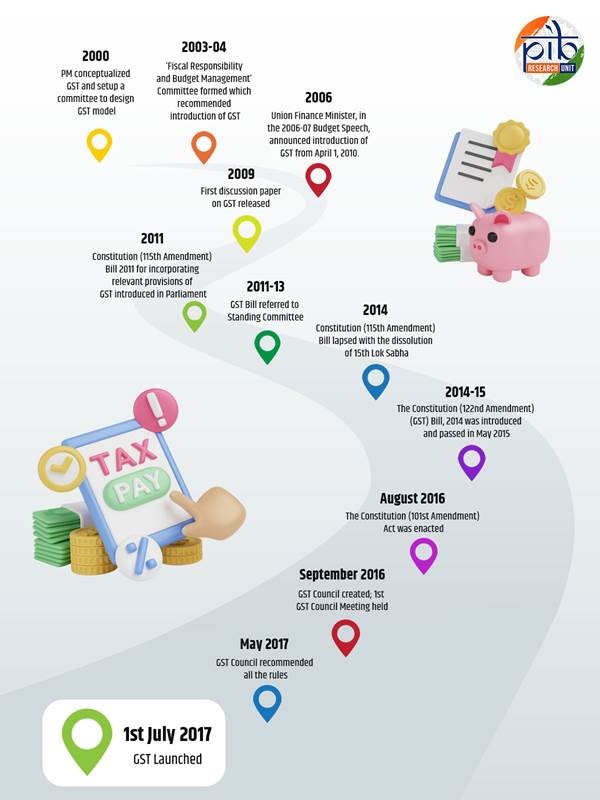
The Journey to GST – Timeline
Key Features of GST
- One Nation, One Tax: GST replaced multiple indirect taxes, creating a unified tax structure across India, and eliminating the cascading effect of taxes.
- Dual Structure: GST includes Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST) with Integrated GST (IGST) for interstate transactions.
- Destination-Based Tax: GST is levied at each stage of the supply chain, ensuring seamless credit flow and reducing the tax burden on consumers.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Businesses can claim credits for taxes paid on inputs, thereby avoiding double taxation.
- Threshold Exemption: Small businesses with turnover below a specified threshold are exempt from GST, easing compliance.
- Composition Scheme: Small taxpayers can opt for a simplified scheme, paying a fixed percentage of their turnover as GST with minimal paperwork.
- Online Compliance: The GSTN portal facilitates easy registration, return filing, and payments, enhancing ease of compliance.
- Anti-Profiteering Measures: The National Anti-Profiteering Authority (NAA) ensures that the benefits of GST are passed on to consumers, preventing unfair pricing.
- Increased Compliance and Transparency: Digital processes under GST curb tax evasion and promote transparency in the tax system.
- Sector-Specific Exemptions: Certain sectors like healthcare and education benefit from exempt or reduced GST rates.
- Account Settlement: The GST system ensures seamless transfer of credits between the Centre and States, maintaining a balanced tax structure.
Significance of GST
Impact on MSMEs:
- Simplified Compliance: GST has significantly eased compliance for MSMEs, with increased thresholds and simplified tax schemes.
- New Financial Avenues: The introduction of systems like TReDS has opened up new opportunities for MSMEs, allowing easier access to credit based on receivables.
- Reduced Compliance Burden: MSMEs now benefit from quarterly return filing options, reducing the administrative burden.
Benefits to Consumers:
- Lower Tax Rates: The average tax rates under GST have decreased, leading to savings for consumers on essential items.
- Increased Compliance: The number of taxpayers has doubled, improving compliance and expanding the tax base.
- Reduced Household Expenses: A study by the Finance Ministry revealed that consumers save approximately 4% on their monthly household expenses due to GST.
Benefits to the Logistics Sector:
- Enhanced Efficiency: GST has streamlined the logistics sector by removing interstate barriers and reducing transport times by over 33%.
- Reduced Costs: Companies no longer need to maintain warehouses in every state, leading to a leaner logistics chain.
- Increased Investment: The logistics sector has attracted significant investment post-GST, boosting demand for high-tonnage trucks and creating employment opportunities.
Accomplishments of GST
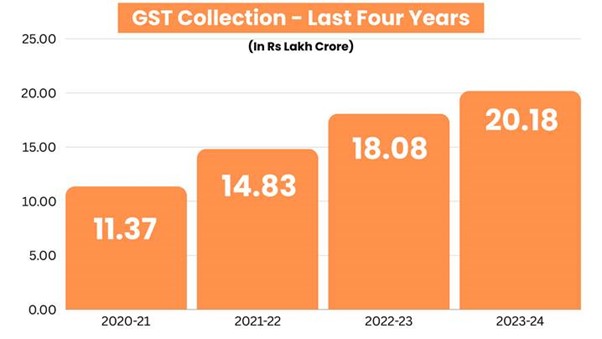
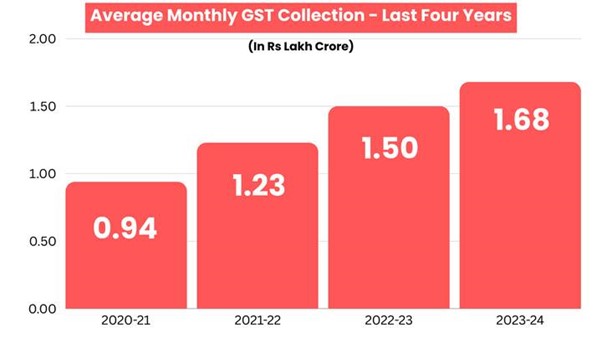
Since its implementation, GST has shown remarkable progress in revenue collection:
- 2020-21: ₹11.37 lakh crores (average monthly collection: ₹0.95 lakh crores)
- 2021-22: ₹14.83 lakh crores (average monthly collection: ₹1.24 lakh crores)
- 2022-23: ₹18.08 lakh crores (average monthly collection: ₹1.51 lakh crores)
- 2023-24: ₹20.18 lakh crores (average monthly collection: ₹1.68 lakh crores)
These figures demonstrate the growing compliance and effectiveness of the GST regime, contributing to India’s economic growth and stability.
Conclusion
The implementation of GST on July 1, 2017, represents a pivotal moment in India’s economic history. Over the past seven years, GST has unified the tax system, simplified compliance, and promoted transparency across sectors. As we celebrate GST Day each year, it reaffirms India’s commitment to building a robust and equitable tax regime that fosters economic growth and global competitiveness.
#GST7Years#GSTIndia#GSTReform#TaxReform#IndianEconomy#EconomicGrowth#TaxTransparency#MSMEsIndia#LogisticsSector#GSTBenefits#UnifiedTaxSystem#DigitalIndia#ComplianceMatters#IndiaTaxSystem#FinanceReform#EconomicTransformation#OneNationOneTax#India2024#ModiGSTReform
